Speakers are the main component of a sound system, and your sound system’s performance greatly depends on your speakers’ specifications. However, when most of us look at a speaker’s specs, we can’t understand most of it. In this guide, we’ll look at the most important speaker specifications and how they improve your sound system.
Frequency Response
What Is Frequency Response?
Frequency Response is a the ability of a speaker to produce sound in different frequency ranges. It is represented by a graph or chart that shows the intensity of the sound output of the speaker at different frequencies.
Frequency Response usually has two main ranges:
High-Frequency Response: This is the frequency response of a speaker in the high range, which includes treble and mid-treble. High-frequency response determines the detail and clarity of a speaker.
Low-Frequency Response: This is the the frequency response of a speaker in the low-range, which includes the bass and mid-bass. Low-Frequency Response also determines how rich the bass will be, as well as it’s depth and power.
Frequency Response And Speaker Performance
Frequency response affects the type of music your speaker is suitable for, for example, pop music has more bass and treble. If you like bass-heavy music, you should get a speaker with a stronger low-frequency response. If you want some more clarity in your treble, a speaker that focuses on high-frequency response is better.
Frequency Response Graphs
Most frequency response graphs have frequency (in Hertz, Hz) on the horizontal axis and the intensity of sound output (in Decibels, dB) on the vertical axis.
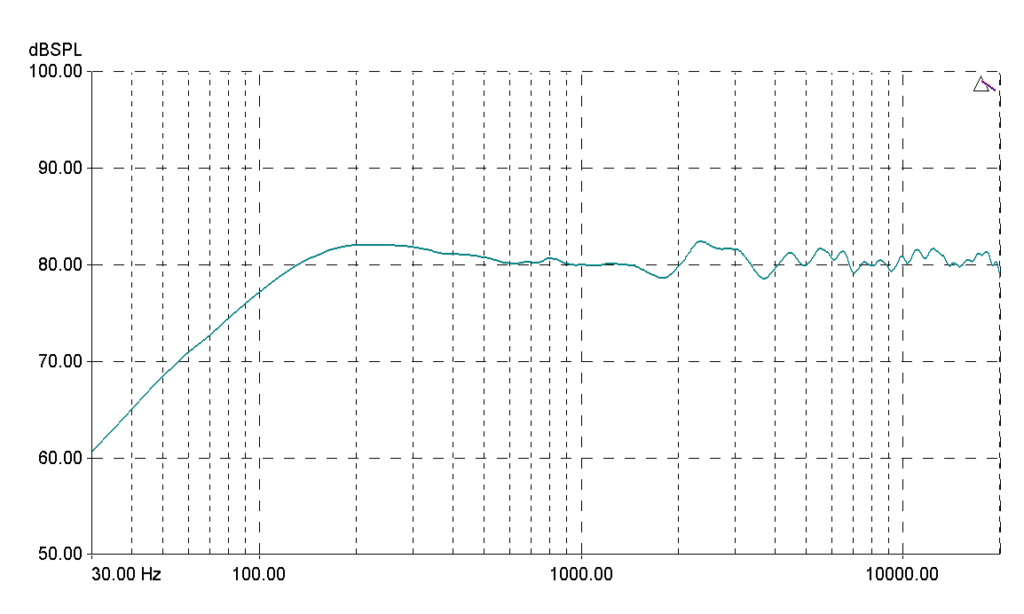
- A flat curve means that the sound output is equal at each frequency.
- A rising curve means that the speaker has a stronger sound output in the high frequency range.
- A declining curve means that the speaker has a weaker sound output in the high frequency range.
- Peaks or dips at a specific frequency mean that at the point the sound output is uncommonly strong or weak.
Sensitivity
Units And Measurements
Sensitivity is measured in decibels (dB). Sensitivity numbers are measured relative to 1 watt (W) of power. So, if a speaker has a sensitivity rating of 80dB, it means that the speaker will produce 80dB of sound when 1 watt of power is supplied. Sensitivity is measured at a constant sound pressure level at a specific frequency; this makes comparison between different speakers easier.
How Does Sensitivity Affect Sound Output
Sensitivity is the intensity of sound produced by the speaker when receiving 1 watt of input power. For the same power input, speakers with high sensitivity will produce greater sound output, and speakers with low sensitivity will produce a lower sound output.
If you have a high-sensitivity speaker, you can choose a low-powered amplifier for your system and vice versa. You should also look at your speaker’s maximum power handling capabilities when buying an amplifier to prevent overdriving. Understanding sensitivity will help you choose a better amplifier for your system and get you the best sound output.
To understand amplifiers better, read our article on Amplifiers And Their Classes.
Impedance
Why Is Impedance Important
In speaker specifications, impedance is a measure of the resistance to current at different frequencies. The impedance of your speakers should match the impedance of your amplifier so that your speakers can reach their full potential with the amplifier. If your impedance does not match, it can cause damage to your system and noise distortion.
Distortion
A speaker can distort or change the original sound it is playing. This reduces the quality and detail of the sound produced. Distortion is often stated in speaker specifications to help users better understand it.
Types Of Distortion
Harmonic Distortion: It is when the sound produced by speakers contains some parts of frequencies that are not in the original audio signal. This can cause sound distortion and affect sound quality.
Cross-Distortion: It is the interaction between different parts of a speaker, causing distortion. When vibration in one part affects the other, it causes distortion at high volumes.
Power Handling
Power handling refers to the maximum power a speaker can withstand without getting distorted. In speaker specifications, power handling is usually expressed in two ways.
Continuous Power: This is the power a speaker can withstand over a long period of time (in hours). At this power level, the speaker can operate continuously without any damage or distortion.
Peak Power: This is the amount of power a speaker can withstand for a small instant (in milliseconds). A speaker can accept power over this level. However, too much time over peak power levels can cause damage and distortion.
Resonant Frequency
This refers to the lowest amount of frequency your speaker can operate at. Resonant frequency depends on the materials and design of the cone and drivers. If your speaker will be producing lower tones, then you’ll want a low resonant frequency.
In conclusion, speaker specifications play a vital role in getting the most out of your sound system. Speakers are the main part of any sound system, and understanding speaker specifications will help you better utilize your speakers.
